FAQs
ARKA Endocrine Clinic
Have an endocrinology-related question? We have the answer. Check out these FAQs and then contact ARKA Endocrine Clinic for more information.
What insurance do you accept?
We accept most commercial insurance plans, Medicare, and self-pay options. Please contact our office directly to confirm if we accept your specific insurance plan.
Why do we get diabetes mellitus (DM)?
Diabetes mellitus occurs when the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells, where it is used for energy or stored for future use. Insufficient insulin or the body's inability to use it leads to elevated blood glucose levels.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus?
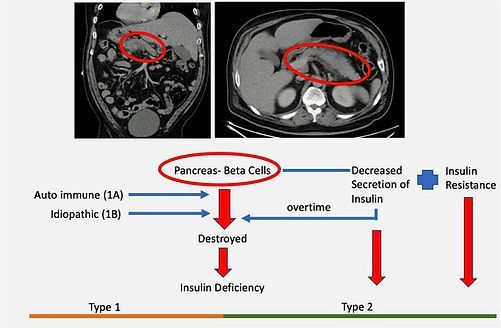
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to meet the body's needs.
What are the common symptoms of DM?
- Excessive thirst, hunger, and urination
- Fatigue, dehydration, and weight loss
What is the screening test for diabetes?
Pre-Diabetes:
- Fasting plasma glucose: 100-125 mg/dL
- OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test): 140-199 mg/dL
- HbA1c: 5.7-6.4%
Diabetes Mellitus:
- Fasting plasma glucose: >126 mg/dL
- OGTT with 2-hour plasma glucose: ≥200 mg/dL
- HbA1c: ≥6.5%
- Classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or crisis with random plasma glucose: ≥200 mg/dL
What is HbA1c?
HbA1c measures your average blood sugar level over the past three months.
- A1C < 5.7% is normal
- 5.7 - 6.4% indicates prediabetes
- ≥ 6.5% indicates diabetes
How do I manage DM?
- Intense lifestyle modifications and weight loss
- Oral medications
- Insulin therapy
What are some of the complications of DM?
- Eye: Retinopathy (damage to blood vessels in the back of the eye)
- Heart: Coronary artery disease (early blockage of heart blood vessels)
- Kidney: Nephropathy (kidney failure), albuminuria (protein spillage in urine)
- Nerves: Neuropathy (pain, tingling, numbness, burning, skin ulcers)
- Brain: Stroke
What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a severe, life-threatening complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, ketosis, and severe dehydration. It can lead to a coma and often requires hospitalization, typically in an intensive care unit, for intravenous insulin treatment. It is often the initial presentation of Type 1 diabetes.
What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy. It can cause complications such as pre-eclampsia (uncontrolled high blood pressure), premature delivery, large babies (risk of clavicle fractures, nerve injuries during delivery, and high risk for a c-section), and stillbirth. Early screening (24-28 weeks of pregnancy) and controlling blood glucose can prevent most complications.
What is continuous glucose monitoring?

Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) tracks your blood glucose levels throughout the day, providing a comprehensive view of glucose trends. Unlike traditional fingerstick methods that offer a snapshot, CGM helps you balance your day by monitoring trends and adjusting medications, diet, and activity. It includes alarms for dangerously high or low glucose levels and stores data that can be downloaded by your physician for better management of your care.
What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is characterized by increased levels of thyroid hormones (Free T4 and T3) and low TSH. Symptoms include heat intolerance, palpitations, atrial fibrillation, weight loss despite a good appetite, nervousness, emotional instability, increased sweating, and menstrual irregularities. If untreated, it can lead to a life-threatening condition called a thyroid storm.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is characterized by decreased levels of thyroid hormones (Free T4) and increased TSH. Symptoms include fatigue, muscle pain, cold intolerance, constipation, weight gain, and menstrual irregularities. If left untreated, it can progress to a life-threatening emergency called myxedema coma.
What is a thyroid nodule?
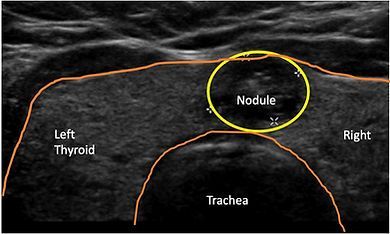
A thyroid nodule is a cyst or outgrowth of thyroid tissue. It is extremely common, and most nodules are benign, with only about 5-15% being malignant.

Share On: